Early Symptoms and Treatments for Deep Vein Thrombosis
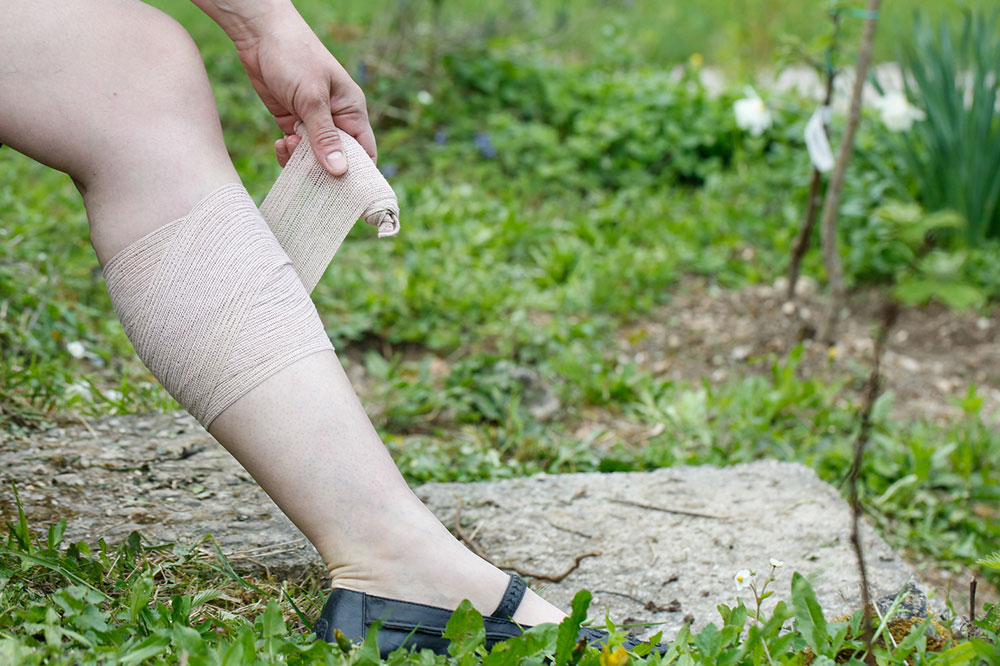
Deep vein thrombosis is the presence of blood clots in the deep veins, usually present in the legs. This condition causes redness, pain, and inflammation which makes mobility difficult, leading to dependence on others that leads to further anger and embarrassment. Causes of the condition can be pregnancy, obesity, injury, or even inherited blood disorders. Pulmonary embolism is a side-effect of this condition which is caused when a part of the clot is broken and travels to the lungs. This can be life-threatening if not treated in time.
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis
In deep vein thrombosis, early warning symptoms include the following:
- Inflammation of the leg affected. Swelling of both legs is a rare condition.
- Discoloration of the affected leg, which appears red in color.
- Severe pain in legs, particularly the calf muscles.
- The affected leg feels warm all the time.
If these early warning symptoms of deep vein thrombosis are left unnoticed, it could lead to them aggravating and ultimately resulting in a pulmonary embolism. The symptoms of pulmonary embolism are as follows:
- Irregular and rapid heartbeat
- Difficulty breathing
- Inability to breathe deeply due to chest pain
- Coughing up blood
- Episodes of fainting due to low blood pressure
- Signs of anxiety
Treatment options for deep vein thrombosis
The main aim of a deep vein thrombosis treatment is to stop the growth of blood clots and to prevent it from breaking loose. The treatment options for the condition depend on a variety of factors. Here are some of the procedures given below.
- Anticoagulant medication: Blood thinners or anticoagulants are mostly used to stop the growth of clots and avoid further clot formation. However, these medicines do not dissolve the existing clots. Anticoagulants should not be taken without a doctor’s advice or prescription. They can be taken in a pill form or the medication can be injected into the veins directly. This treatment procedure tends to last for at least three months — it is crucial to stick to the exact timeline as advised by the doctor.
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter: Blood thinners cannot be prescribed to some individuals due to the risk of excessive bleeding. These individuals would require an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter. This procedure is done by inserting a filter into the inferior vena cava, which is the large vein present in the abdomen. This helps in filtering blood clots and prevents it from traveling to the lungs.
- Thrombectomy: In chronic cases of deep vein thrombosis, thrombectomy is performed to dissolve or remove the clot.
In cases wherein surgery is not possible, a clot-buster called TPA thrombolytic medication is given, to break down the clots formed in deep vein thrombosis.